Let’s clear this up right now, strength training and running go together, it’s not one or the other. Most runners avoid strength training for fear of being bulky, or because they’re afraid it will decrease their run time. Runners need to understand that strength training can improve their run time and increase their work capacity. If that’s not convincing, then consider that runners are prone to injuries such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, plantar fasciitis, stress fractures, as well as hip, low back, and shoulder pain. Quite an extensive list. We can prevent these issues by introducing kettlebells into our training.
Why Kettlebells?
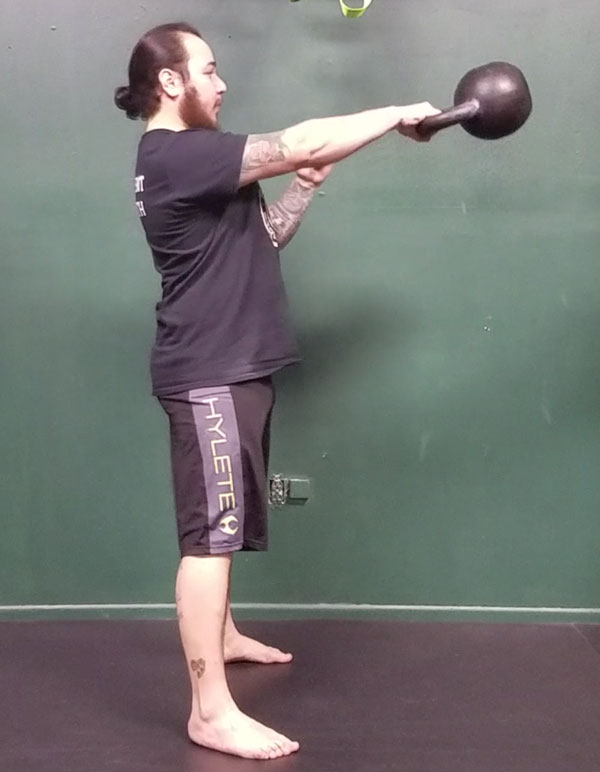
The kettlebell is the Swiss Army knife of fitness—you can train for strength, conditioning, mobility, power, etc. with just one tool. A tool that serves multiple purposes is great if you have limited time or not enough space for bigger equipment like barbells or racks of dumbbells. Kettlebells give you the ability to exert a maximum muscular contraction instantly in an explosive power burst. Using exercises like the kettlebell swing or kettlebell snatch will train you to build a lot of power. The amount of tension, speed, and force needed to complete a swing or a snatch is very high, and the benefits carry over into the production of power. Kettlebell exercises have been known to help athletes improve their performance by increasing their power output—this also allows runners to excel in their races.
When training with kettlebells, we are often barefoot or wear minimalistic shoes. At my facility Restored Strength, we highly recommend that our members do not wear shoes. We are in shoes all of the time, and wearing shoes while training puts the foot in a plantar flexed position because the heal is elevated. Because of compression from the shoes they can also restrict the range of motion in the ankle. The freedom of being barefoot allows the ankle to have a greater range of motion. Training barefoot will also raise your kinesthetic awareness by allowing the proprioceptors in the foot to have greater exposure. The benefits can transfer over to your running, when you are not constricted by your shoes.

Why Strength Training Can Prevent Injuries
The RKC is well known for being The School of Strength. We promote the importance of strength in a purposeful manner. While strength training has many applications, let’s discuss why it is essential to be a strong runner. When you begin to introduce strength training into your program, you get physically stronger and there’s a physiological aspect as well. Strength training promotes greater bone density which reduces the likelihood of hair line fractures. You will also strengthen the ligaments, tendons, and muscles—which hold and secure joints in proper alignments. If you are not strength training, the certain areas in the body will become weak. Being weak is dangerous since weak muscles and bones are fragile and susceptible to injuries.
Strength training can increase your muscular work capacity, which can improve your running technique. You’re less likely to fatigue, and when your muscles are stronger, you can maintain proper mechanics for longer periods of time. Stronger muscles will decrease the likelihood of fatigue during a race, and strength training helps increase the type 2 (fast twitch) muscle fibers. Focusing on the big five major muscle groups—knees, hamstrings, glutes, trunk, back—used when running will make strength training less daunting.
What to Train
Glutes: The glutes are the key muscle group in the mechanics of running. The gluteus medius will be the main focus, as this muscle is the rotator cuff of the lower body. When you move, it’s the first muscle to quickly contract, and it stabilizes your body when you are on one leg. Running is a unilateral activity—a single leg is in motion—which is why it’s crucial to strengthen and stabilize the gluteus medius in unilateral exercises.
Hamstrings: These bad boys strengthen your lower back. When they contract, they flex the knees, the repetitive motion in running. Your heel should reach your glutes during the back-swing motion, this allows for greater power output when running. With stronger hamstrings, you will be able to produce greater force output when running. Having strong hamstrings will complement your glutes—the two together will prevent low back pain and allow your running to be less strenuous on the posterior chain.
Quadriceps: Runners usually have overdeveloped quadriceps, but it is still worthwhile to train them. The quadriceps are responsible for two major movements in running, knee extension and hip flexion. These actions cause the leg to swing forward when running. The insertion of the quadriceps is located on the tibial tuberosity, the boney projection below the knee. Having stronger quadriceps will assist in maintaining knee position. One muscle of the quadriceps, the vastus medialis, helps stabilize the patella and the knee joints when we run.
Trunk: The trunk is a fancy word for abdominals. The trunk maintains your posture and keeps you upright. When we run, we want to maintain a tall posture and make sure that we are as tall as we can get, allowing us to have a greater range of motion through the hips. We won’t be able to maintain that tall position while running with a weak trunk. Strengthening the abdominals will allow for greater stability. Stronger abdominals also reduce the wobbly feeling when running. If you are wobbling from side to side when you run, then you have an energy leak slowing you down.
Back: The back is the last key player for strong running. Like the trunk, the back has the same role of keeping your body upright. Having a stronger back will help retract the shoulder blades, which prevents the shoulders from rolling forward. Good posture carries over to proper mechanics when running. If you find it difficult to maintain your posture, then you will need to improve your back strength. A strong back can prevent energy leaks through the upper body, and make sure you’re carrying your arms in an optimal way while running. A strong spine complemented by strong mid and lower backs will stabilize the spine and the pelvis.
How to Train
When we train, we want to train movements rather than muscles. The big movements are lower body pushing and pulling, upper body pushing and pulling (vertical and horizontal), trunk work, carries, and unilateral upper and lower body movements. I make mobility training a staple in my programming as well. It is a mixture of movement and strength—you need to be mobile to be strong and you need to be strong to be mobile.
In my opinion, the push/pull upper body/lower body approach is the most optimal way to train. It conserves time and targets every area. Using this type of training will also reduce the amount of training sessions each week. I recommend two to four days each week, depending on your training.
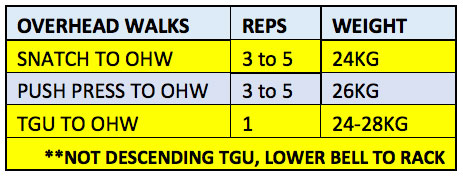
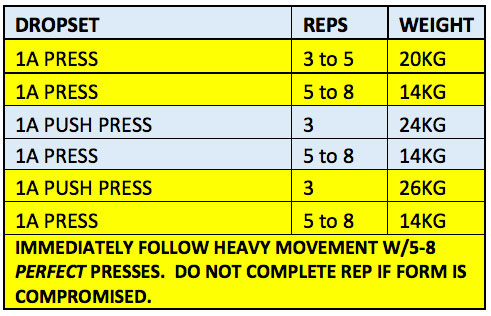
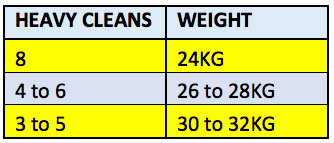
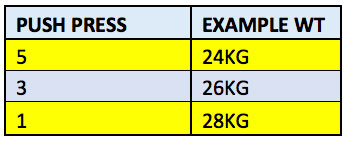
Training day example:
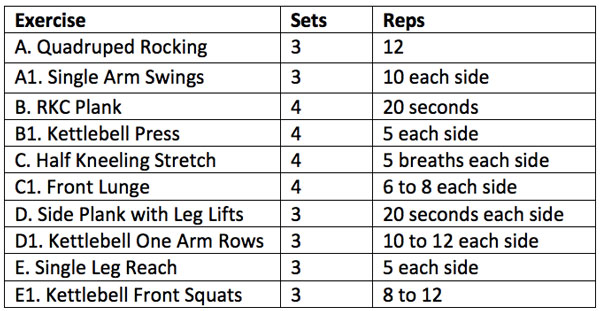
Conclusion
Strength training can undoubtedly improve your run time and prevent injuries if done correctly. There are many different modalities of training, and kettlebells have been the most useful for me. To help your athletic performance, make sure to include kettlebell training in your program. If you are unfamiliar with kettlebell training, find yourself a certified RKC instructor to take your training further.

****
William Sturgeon, RKC II trains clients at his gym, Restored Strength. Contact him through his website at RestoredStrength.com or follow him on Facebook: facebook.com/restoredstrength
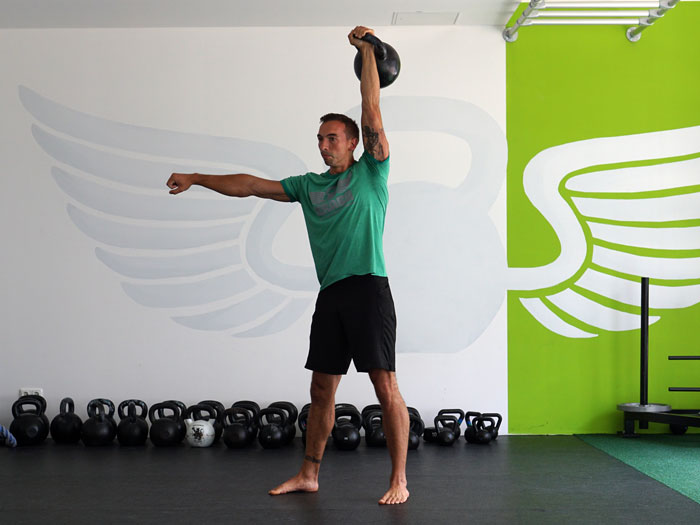
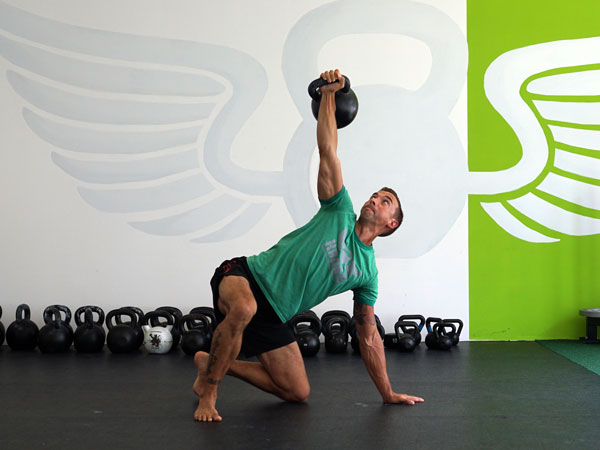
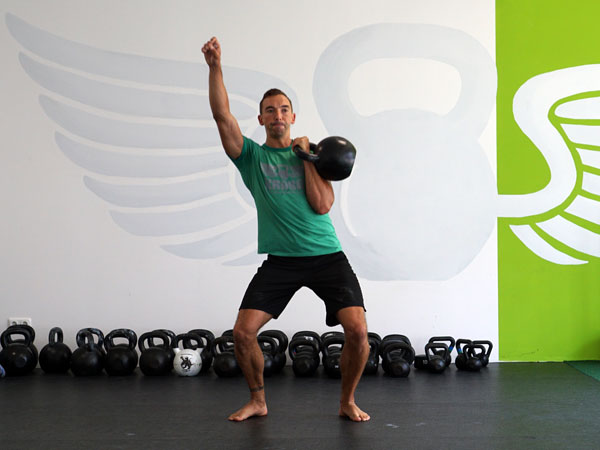
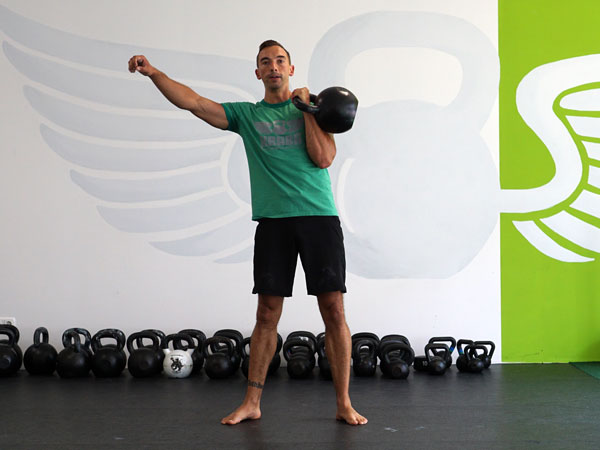
















 The RKC is known as the School of Strength because we educate candidates on how to teach strength to others. As we all know the
The RKC is known as the School of Strength because we educate candidates on how to teach strength to others. As we all know the