If it wasn’t for kettlebells, I would not be a chiropractor today. I started out with the RKC in 2006 and attended the CK-FMS in 2010. The CK-FMS was the movement program that was based off of the FMS and was taught by Gray Cook and Brett Jones of FMS. It introduced me to movement screening and how to help clients move better, feel better and live better pain free.
 I ran my gym based on what the FMS taught. We used the Functional Movement Screen as part of our onboarding program. I loved the results we were getting in members that could not/did not move as well as they should. It started my journey from Law Enforcement/Gym Owner to attending Chiro school. I knew that there was more that I could do to help people with the right credentials, and being a Chiropractor was something that I knew would allow me to help more people achieve even better outcomes.
I ran my gym based on what the FMS taught. We used the Functional Movement Screen as part of our onboarding program. I loved the results we were getting in members that could not/did not move as well as they should. It started my journey from Law Enforcement/Gym Owner to attending Chiro school. I knew that there was more that I could do to help people with the right credentials, and being a Chiropractor was something that I knew would allow me to help more people achieve even better outcomes.
The ability to look at and screen movement helped tremendously in Chiro school. It allowed me to look at everyone through a movement lens versus just looking at the injury that brought them in. I attended the Selective Functional Movement Assessment certification while in school. That is the clinical variation of the Functional Movement Screen. It allowed me to narrow in on the root cause of the patient’s dysfunction. The RKC/FMS gave me a leg up in the Rehab and improving outcomes.
Fast forward a few years and I am still helping people with better movement and decreased pain with kettlebells. Kettlebells are a significant part of our rehab program. They take up little space and can be used by everyone. The allow us to engage our patients in their rehab due to the challenge and the fun of using the kettlebell. Everyone that walks in wants to try and pick up the 106lb…
We use the skills taught at the Hardstyle Kettlebell Certification (HKC) as our base for rehabilitation and strengthening. You will often hear that the swing, Get Up and squat pretty much fix what ails you. Guess what? It is true. We find that if our patients have those three exercises down, their activities of daily living as well as any extracurricular activity can be performed with little to no dysfunction. Can we fix everything? No, but we can help them improve their lives and make them more injury resistant.
One of our patients, a CrossFit competitor, had to undergo shoulder surgery for a tear. Once we were able to load and stress the shoulder, we started out with the unweighted get up. We started out with rolling to the press. This allowed us to help connect her core to the rest of her body core after six weeks of being sedentary. We performed the movement of rolling to the press without weight. She would lay on her side in the fetal position, roll to supine and press from the floor.
Once she owned the movement, we move to shoulder packing. We use the supine press position and showed her how to pack the shoulder. We accomplished this by lightly pushing and pulling the arm up and down int the press position. This allowed her to feel the movement and perceive what it should feel like when doing correctly. We also showed her to rotate her fist in the press position for movement in the joint. This was for getting fluid moving as well as allowing the body to feel what the shoulder should be doing when functioning correctly.
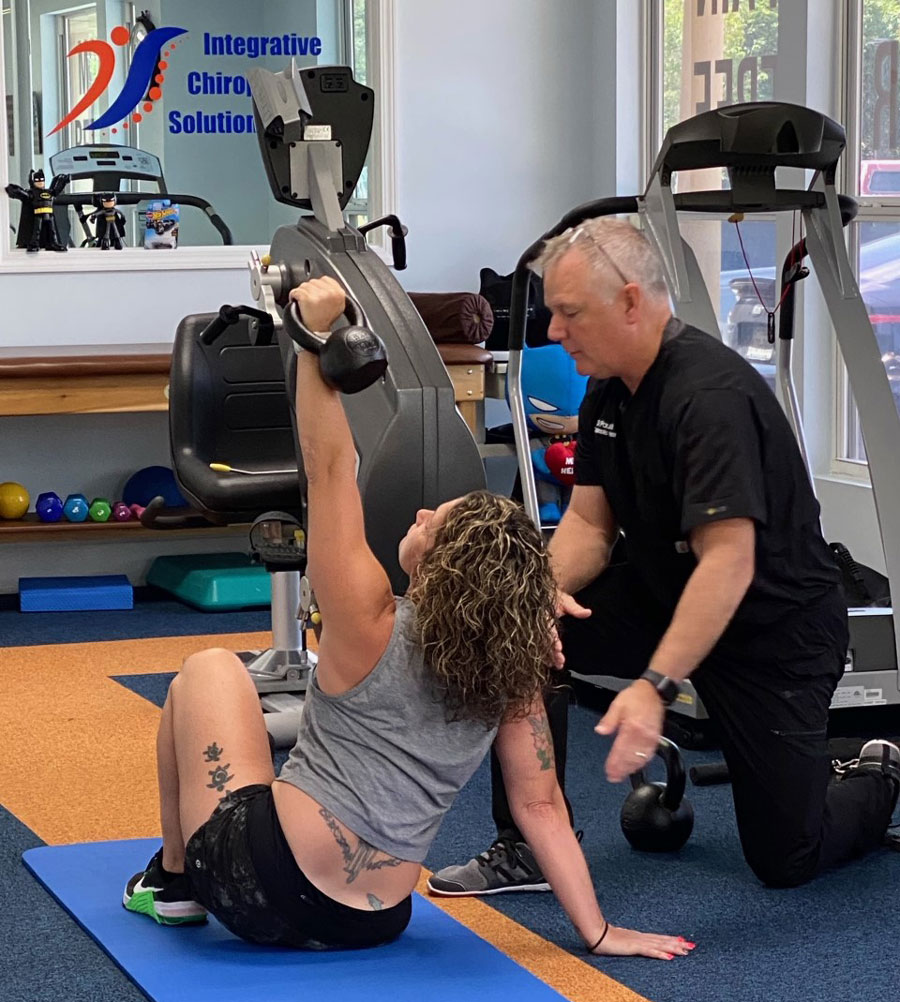

We like to work the standing to half kneeling after teaching the shoulder packing to get to half kneeling and help with stability. I find that this is often easier to teach than having patients work into the post and to the heist and windmill before they can safely move through the mid-range movements. There is no set number or time frame. We have had one patient work through the parts of the get up unloaded for 6 months before they were allowed to use any weight. Time practicing the get up is never wasted time.
The athlete worked through the rest of the get up without weight and then started with low loads. We moved from 25% internal rotation and 50% abduction to 100% pain free in both ranges of motion in 12 weeks after surgery. She is back to competition weights without pain or dysfunction.
The swing can be used in the same manner. We find the parts of the swing that will benefit patients and work from there. The power of the teaching process and the techniques are often greater than the sum of the swing. For back pain, posterior chain strengthening has been shown to be superior to general exercise and walking programs for treating chronic low back pain. (1)
The swing is a great tool for working with patients with issues in the back. For back pain we start with the basics, breathing. We start with crocodile breathing as taught in the HKC and RKC. A large problem that we find with low back pain and other injuries are breathing dysfunctions. A large portion of our patient base breathe in the upper chest, using traps and accessory muscles to breathe versus the diaphragm. Breathing has been shown to help inhibit the paraspinal muscles and help with spasms. Proper breathing patterns help with balance, pain and the ability to access full strength in a patient. (2)
Proper breathing is essential for being able to develop the ability to use tension and relaxation to get the most out of swings. What do we do, we work on teaching them how to breathe properly. Once they understand how to breathe, it becomes an alert system for us. If they lose the ability to breathe well during an exercise, we have either fatigued them or selected the wrong exercise to use.
The deadlift, the deadlift drag, and the pendulum swing are three of the swing teaching tools that we use a lot. “Deadlifts have been shown to improve low back pain as effectively as low load motor control drills.”(3) That basically says that if the patient is ready, deadlifts are at least as effective as bands, stick drills and similar movements that do not require loads.
Why not make them stronger if it is clinically available to the patient. There is a lot more buy in from the patient when they have that visceral response from lifting real weight and getting stronger each session.

The deadlift drag is a great tool for strengthening the posterior chain and connection it with movement. The set up is deadlift hinge with the bell in front. The kettlebell is moved along the ground in a drag utilizing the lats, rhomboids and other muscle of scapular control as well as erectors and glutes. It has helped us to improve scapular control and function in patients that have scapular dyskinesia.
I have personally used the pendulum swing in my own rehab journey. I suffered a disc injury several years ago that kept me from performing standard exercises. I was able to move into a hip hinge but could not move through the full deadlift pattern with weight. I found that the low position was pain free and I was able to swing a kettlebell in that position. I would get into the hip hinge at a position that did not hurt or worsen my symptoms and perform pendulum swings.
Our end goal with swings is to move through two handed to one-handed swings. Research has shown that this is a great way to help mitigate current back pain as well as help decrease future problems. The one hand swing engages the opposite side spinal erectors and same side external obliques leading to greater stabilization in the back and core.(4)
A specific end user for the Kettlebell Swing as a rehab tool is our Post ACL reconstruction patients.(5) The research has shown that kettlebell swings help decrease the risk of non-contact injuries from high risk to a lower risk profile after 6 weeks of training. We teach them the Get Up, before we allow them to swing. The Get Up is used as a strengthening and screening tool to ensure the patient can load the knee safely before transitioning to the swing. The improvements are due to posterior chain strengthening, the semitendinosus and hamstrings.

The squat as taught in the HKC/RKC are useful in several ways. We like the squat as the end game for connecting the dots of the rehab program. It requires mobility and stability to perform and control of the breathing and tension. We use Bottoms Up Squats to test for connectivity of the core with the movement pattern. If the Bottoms Up Squat cannot be performed, there is a leak in the pattern.
We want to make sure that our elderly patients can get off the floor and the toilet. If they can do that, we have increased their quality of life and survivability. We have found that patients that have gone through the program have reached those goals.
This is a quick look at how you can implement kettlebells in the clinic to help your patients move better, feel better, live better pain free. It does not have to be complicated to work.
***
Paul Britt DC is a Certified Chiropractic Sports Physician and Senior RKC based in Gulf Breeze Florida. His practice, Integrative Chiropractic Solutions utilizes kettlebells as rehabilitations tools to help his patients achieve their goals.
- Tataryn N, Simas V, Catterall T, Furness J, Keogh JWL. Posterior-Chain Resistance Training Compared to General Exercise and Walking Programmes for the Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain in the General Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med Open. 2021 Mar 8;7(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40798-021-00306-w. PMID: 33683497; PMCID: PMC7940464.
- Stephens RJ, Haas M, Moore WL 3rd, Emmil JR, Sipress JA, Williams A. Effects of Diaphragmatic Breathing Patterns on Balance: A Preliminary Clinical Trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017 Mar-Apr;40(3):169-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Mar 1. PMID: 28259495.
- Aasa B, Berglund L, Michaelson P, Aasa U. Individualized low-load motor control exercises and education versus a high-load lifting exercise and education to improve activity, pain intensity, and physical performance in patients with low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015 Feb;45(2):77-85, B1-4. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2015.5021. PMID: 25641309.
- Andersen V, Fimland MS, Gunnarskog A, Jungård GA, Slåttland RA, Vraalsen ØF, Saeterbakken AH. Core Muscle Activation in One-Armed and Two-Armed Kettlebell Swing. J Strength Cond Res. 2016 May;30(5):1196-204. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001240. PMID: 26473519.
- Zebis MK, Andersen CH, Bencke J, Ørntoft C, Linnebjerg C, Hölmich P, Thorborg K, Aagaard P, Andersen LL. Neuromuscular Coordination Deficit Persists 12 Months after ACL Reconstruction But Can Be Modulated by 6 Weeks of Kettlebell Training: A Case Study in Women’s Elite Soccer. Case Rep Orthop. 2017;2017:4269575. doi: 10.1155/2017/4269575. Epub 2017 Jan 18. PMID: 28197354; PMCID: PMC5286491.