
Although many good articles have been written about squatting, coaches are still frequently confronted with “do not go below parallel or 90°”, “you shouldn’t bring your knees past your toes”, or “squats are bad for your back”. Given these controversies and the fact that the squat is one of the fundamental exercises for RKC kettlebell training, the purpose of this article is to review the most important aspects of this exercise.
The squat is versatile—it has been shown that a 1RM squat is highly correlated to jump and sprint performance (Wisløff et al., 2004) and it can improve knee stability through a development of tighter joint capsules (Chandler et al., 1989). It is particularly useful for training athletes, but can also help improve strength and functionality in non-athletic populations. Squats improve the function of the gluteal muscles which will prevent injury or decrease back pain. Squats can also help everyone with daily tasks such as lifting items from the ground, or climbing stairs. It is important to note that research has not been able to establish a relationship between (deep) squatting and a greater risk of knee and back injuries, given that the exercise is performed with proper technique (Meyers, 1971; Panariello et al., 1994; Steiner et al., 1986; Hartmann & Wirth, 2014).
Squat Depth
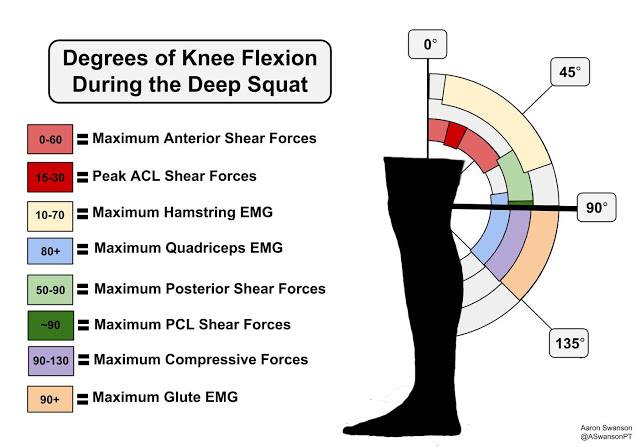
Li et al. (2004) showed that the greatest stress on the posterior cruciate ligament during squatting occurs at around 90° of knee flexion. The authors further stated that deep squats help to constrain the knee joint and significantly reduce anterior and posterior tibial translation as well as tibial rotation compared to smaller flexion angles, thereby reducing the stress on the cruciate ligaments. Li et al. (2004) also found “the tolerance to load is enhanced in the deepest portion of the squat with a protective effect conferred to ligamentous structures”. This is in accordance with other researchers (Kanamori et al., 2000; Li et al. 1999; Sakane et al. 1997) who observed reduced stress on the crucial ligaments for knee flexion at angles greater than 90˚.
Caterisano, et al. (2002) looked at the relationship between squat depth and activation of the gluteus maximus and found no difference between partial and parallel squats. However, they reported significant increases in gluteus maximus activity during the deep squat. Given the high incidence of hip osteoarthritis in former elite athletes, and the correlation with reduced passive ROM in hip-flexion (L’Hermette et al., 2004), deep squats may be a useful tool in the prevention of hip-osteoarthritis by improving hip flexion. In summary, there is evidence to suggest that squatting below 90° with proper technique reduces stress on passive structures such as the cruciate ligaments and can have a protective effect in regard to hip and lower back health.
Squats and Injuries
Tibiofemoral compressive peak occurs at 130° of knee flexion and the menisci and articular cartilage will bear significant amounts of stress (Nisell & Ekholm, 1986). As peak patellofemoral compressive forces occur at or near maximum knee flexion, those with patellofemoral disorders or acute injured menisci should avoid high degrees of knee flexion (Sakane et al., 1997; Escamilla et al., 2001). With regard to the cruciate ligaments, Li et al. (2004) concluded, “For those with existing injury or previous reconstruction of the PCL, it is best to restrict flexion to 50° to 60° so that posterior shear is minimized”. “However, there is little evidence to show a cause-effect relationship implicating an increased squat depth with injury to these structures in healthy subjects” (Schoenfeld, 2010).
Knees Over Toes
List et al. (2013) showed that restricting the amount of ankle motion (knees not allowed over toes) led to a smaller ROM at the knee, higher changes in the curvature of the thoracic spine, and higher segmental motions within the trunk. Consequently, the stress placed on the back increased when ankle motion was restricted. This is in agreement with other research, “Although restricting forward movement of the knees may minimize stress on the knees, it is likely that forces are inappropriately transferred to the hips and low-back region. Thus, appropriate joint loading during this exercise may require the knees to move slightly past the toes” (Fry et al., 2003). Escamilla (2001) came to the conclusion that significant strength and sagittal plane mobility is required at the ankle for proper squat performance.
****
Felix Sempf, RKC, PhD Candidate, M.A. Sportscience, trains and instructs at the FIZ in Göttingen, Germany. He can be contacted by email at: felix.sempf@sport.uni-goettingen.de and his website: kettlebellperformance.de